VPNs and VPSs, networks and servers, it’s all that same internet stuff, especially when they’re both virtual and private, right? Well, no.
At first glance, you might think that a virtual private network (VPN) and a virtual private server (VPS) are similar. The truth is, they have nothing to do with one another.
Table of contents
VPS vs. VPN: a side-by-side comparison
The main difference between a VPN and a VPS is that a VPN is a privacy technology, and a VPS is a server you can rent for hosting. Here’s a quick rundown of their differences:
VPS | VPN | |
|---|---|---|
What is it? | A server for rent | A cybersecurity technology |
What is it used for? | For hosting applications and websites | As a service for online privacy and security |
What are its benefits? |
|
|
What is a VPS?
A VPS (Virtual Private Server) is a physical server that has been divided into smaller virtual servers for people to use. Think of a VPS as a shared house with several rooms where a different tenant occupies each space. In this analogy, the house would be the physical server, and each room would be a virtual server.
Not to be confused with a VPC (Virtual Private Cloud), these virtual servers are for rent if you want to host blogs, apps, or other services. However, a virtual private server is “private” to you, meaning you don’t have to share server resources like bandwidth and RAM with other users. In our house analogy, it would be like having a separate room in a house with your bathroom and a kitchen. Pretty neat, huh?
So, why exactly would you rent a private virtual server?
If you only need to host one website or a few business applications, then it’s far cheaper to rent a web hosting service than to get a server that you will need to manage yourself. What’s more, hosting a high-traffic website on your own device will consume lots of your personal device’s CPU (A Central Processing Unit or the main processor). By renting a server, you’ll be able to enjoy an unchanged device’s performance while your clients, readers, etc., will get a speedy experience with your business.
Renting a server for web hosting can be done on shared, dedicated servers or VPS servers.
To compare the three, shared servers are used by multiple clients at once, making them cheaper but slower. Dedicated servers are assigned to only one client, so they perform faster but can be pretty pricey. VPS stands somewhere in between shared and dedicated servers. VPS hosting has multiple clients, but each client has a personal virtual server. How is that possible?
How does a VPS work?
VPS works by using a complex process called virtualization. In simple terms, virtualization takes one physical server and splits it into many virtual servers. The whole creation then functions like an apartment complex with many flats fully isolated from each other. All apartments are still under the same roof and share the same building, yet, they all function independently, each with its entrance or kitchen.
Well, in the case of a VPS, each virtual server has its own hard disc, CPU, and other resources instead of a kitchen. But why would you need a server like this?
What is VPS used for?
VPSs are most commonly used for website hosting. Usually, you’d want one when you need anything hosted on a server.
Here are a few scenarios where you might want to use a virtual private server:
- You are running a powerful application that requires a lot of CPU;
- You host a high-traffic website and need more resources for better performance;
- You are hosting a website with an eCommerce platform and need it to run smoothly;
- You need to run applications or software remotely;
- You need scalability as your business grows.
If you find yourself in any of these situations, VPS will come in handy for you, but are there any more reasons to consider it?
What are the benefits of using VPS?
If you are thinking about renting a private virtual server, here are some benefits to consider:
- With a VPS, you get a personal virtual server and don’t have to share resources with other website owners as you would with a shared physical server;
- It makes your hosting easier to scale and more customizable;
- It’s not as complicated as managing a dedicated server;
- It’s very customizable to your needs;
- It’s cheaper than dedicated servers.
VPS service is beneficial if you’re looking for a way to boost your business, but what if you wish to secure your daily online activities? VPN is the answer!
What is a VPN?
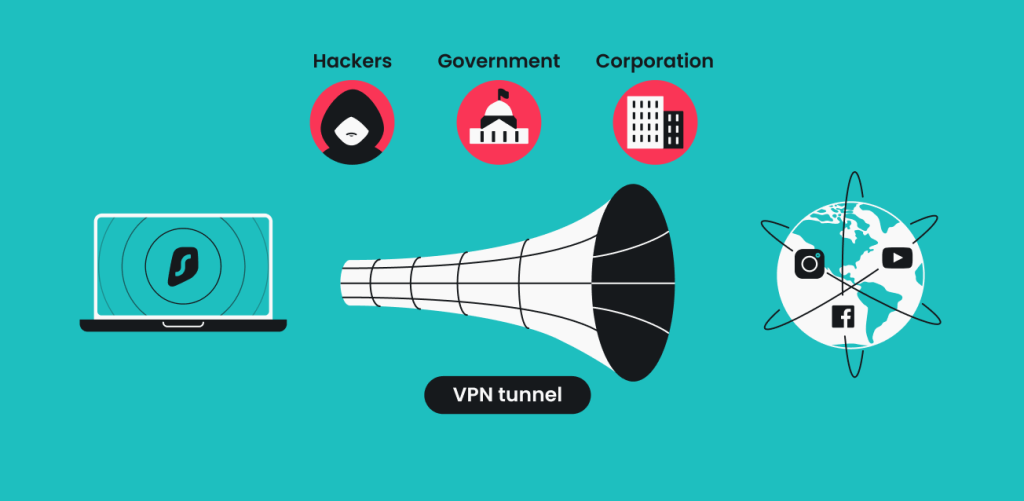
A Virtual Private Network is a broad term for cybersecurity technology.
A VPN usually comes in the form of an app or software. Connecting to it creates an encrypted (secured) tunnel between your device and a VPN server. This server acts as a security layer between you and the web. You could say that you’re browsing the internet through a VPN server.
When should I use a VPN?
VPNs are generally more for private use to help people enhance their online privacy. Here are some examples of when you should consider using a virtual private network:
You’re on public Wi-Fi.
Being connected to public Wi-Fi without any security measures could give hackers access to your data. Encrypting your internet traffic, a VPN hides your data from anyone trying to snoop on your connection.
You want to browse privately.
A VPN makes it nearly impossible to detect you online. This way, your ISP, the government, and other prying eyes can’t spy on what you’re doing.
You want access to geo-blocked web content.
News sites, social, or other types of media can be blocked based on your location for various reasons. However, you can access restricted web content by virtually moving to another country with a VPN.
You want to avoid price discrimination.
Prices for airline tickets, rentals, and hotel rooms vary based on location. VPN software lets you change your virtual location by connecting to a different server. Then, you can compare prices and use a VPN to get cheaper flights, more offers, and better deals overall.
You want to avoid targeted ads.
Targeted ads are annoying. You are targeted based on the data websites collect about you while you browse. A VPN server changes your IP address every time you connect, making tracking your data much more difficult.
What are the benefits of using a VPN?
VPNs have several benefits. Simply put, a VPN protects your online privacy, freedom, and security by:
- Keeping you safe while connected to public Wi-Fi;
- Hiding your IP address;
- Allowing you to avoid government censorship and access restricted web content;
- Hiding your browsing activity by encrypting your internet traffic;
- Preventing your Internet Service Provider, ad brokers, or other malicious entities from tracking, recording, and selling your internet traffic and private information;
- Generally allowing you to browse with peace of mind.
So what should you use, a VPN or a VPS?
Is a VPN better than VPS?
Let’s compare apples to oranges for a bit: one’s orange, the other one’s red; one segments easily, the other doesn’t. How are they similar? They’re both round and edible.
The same idea applies to VPNs and VPSs. They’re two completely different things, but they’re both technologies. One is for hosting (VPS), and the other is for privacy (VPN).
However, there is one case where a VPN and VPS overlap. That is, if you’re looking to access websites only available in a specific country, both can help you. You can rent a VPS in that country and use it to bypass the restriction. Or, you can get a VPN and connect to your desired location with a simple click of a button to get the same result.
Which one’s better? We’ll leave the decision to you!
So, VPS vs. VPN – are they different? Yes, very.
While both are helpful in the online world, they are vastly different.
To sum up, a virtual private server (VPS) allows you to rent out a virtual space for hosting websites and applications with more control than a typical shared server.
A virtual private network (VPN) encrypts your online activity, allowing you to browse privately and secure your personal data.
Interested in learning more about VPNs? Yay! They’re kind of our thing.
FAQ
Can I use a VPS as a VPN?
No. A VPN (Virtual Private Network) and a VPS (Virtual Private Server) are two different technologies. VPNs will secure your activities online by making you invisible, while VPS is a server you can rent to host your service.
However, these two technologies can be combined and used together. You can use a VPN to secure your virtual private server.
Can VPS be traced?
Yes. VPS is a server, and it won’t hide your location. Some VPS do offer services to mask your activities. However, to fully secure your connection and make your VPS untraceable, you can install a VPN on it.
Why do I need a VPS?
You might need a VPS if you’re planning on hosting a service or a high-traffic website. VPS will give you more resources for better website performance, yet, it won’t ensure security online.
If you’re looking for an online security solution, you’re looking for a VPN, such as Surfshark.



