If you’ve ever peeked into the Windows Task Manager, you’ve probably noticed svchost.exe gnawing at your system resources in the background. But what exactly is it doing? Could svchost.exe be a virus?
In this article, we’ll explain what svchost.exe does, how it works, and whether it can pose a threat to your system. You’ll also learn how to monitor its activity and remove any malicious processes that may appear.
Table of contents
What is svchost.exe?
svchost.exe is a Windows system process that is in charge of essential operating services. Windows uses the svchost (short for service host) executable to load and run various background tasks related to managing your network, handling updates, and keeping your system secure. It does this through dynamic link libraries (DLL files) that can be shared among multiple programs simultaneously, reducing the amount of duplicated code.
svchost.exe is designed as a shared service process, meaning it can run multiple Windows services in each instance. This allows for grouping services into logical units based on their function, helping them run more efficiently and reliably.
The evolution of svchost.exe
Older versions of Windows ran fewer svchost.exe instances, which meant that the services bundled under them were usually unrelated. A failure in one service could snowball into crashing the entire group, freezing the operating system, and making troubleshooting particularly difficult.
In Windows 10 and 11, however, Microsoft has taken a more granular approach. Instead of grouping all Windows services together, clusters are now much smaller and more select. This greatly reduces interdependence, benefitting users by:
- Improving fault isolation: if a single service within a svchost.exe instance crashes, it no longer disrupts unrelated services, improving overall system stability;
- Easier troubleshooting: with fewer services per svchost.exe process, it’s now easier to trace high resource usage or faulty behavior back to a specific service;
- Enhancing security: grouping Windows services into dedicated instances makes it harder for malware to compromise multiple system components at once.
What does svchost.exe do?
svchost.exe is designed to keep things running smoothly without needing your attention. Behind the scenes, however, it’s a real powerhouse, as it:
- Handles critical system functions: from network services to Windows updates to system maintenance tasks, svchost.exe plays a key role in keeping your operating system stable and functional. It helps manage the background processes of Windows Defender and Firewall, as well as automatic updates — services you rely on;
- Boosts security and reliability: by organizing services into separate instances, the service host process makes your system significantly more secure. If one service crashes, the rest won’t follow, and your computer keeps running without interruption;
- Improves resource sharing and system efficiency: because Windows uses svchost.exe to run multiple services simultaneously, the impact on memory and processing power is reduced, and overall performance is smoother.
Is svchost.exe safe? How can you tell?
In most cases, svchost.exe is harmless. That is, as long as it’s legitimate since cybercriminals can hide malware behind it. Because the service host process runs multiple instances by design, using svchost.exe as a filename for malware is a fairly easy way to blend in.
Here’s how you can tell if svchost.exe is safe or something more sinister:
Check the file path
Legitimate svchost.exe instances always originate from the C:\Windows\System32 folder. If you find service host processes running from any other location, especially C:\Users or C:\Program Files, you’re most likely dealing with malware in disguise.
Examine digital signatures
A legitimate service host file will always be signed by Microsoft. You can verify this by right-clicking on svchost.exe in Task Manager, selecting Properties, and navigating to the Digital Signatures tab. If the Microsoft signature is missing, you might be in trouble.
Monitor resource usage
svchost.exe typically runs multiple instances, but if one is hogging a significant amount of memory or processing power, there’s probably something wrong. High resource usage from a single svchost.exe process can point to a hidden virus or malware.
Run a full system scan
Even if you don’t notice anything suspicious, running a full system scan using a trusted antivirus or anti-malware tool is a good idea. Security software can help detect if svchost.exe has been compromised by malicious code.
Check the services attached to svchost.exe
Use Task Manager to see which services are running under each svchost.exe instance. To do so, right-click on a svchost.exe process and select Go to Services. If you see services you don’t recognize or ones that seem out of place, consider performing an antivirus scan.
How to guard against svchost.exe malware
Although svchost.exe is generally safe, verifying your processes is always smart, especially if they look suspicious. Here are some steps you can take to keep your computer safe:
- Use security tools: antivirus software and VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) are essential for online security, and you can get them both with our Surfshark One plan. Antivirus monitors your system in real-time, detecting all attempts to masquerade malware as legitimate files. A VPN adds a layer of encryption to your internet connection, shielding you from cyberattacks;
- Monitor the Task Manager: regularly check your Task Manager for svchost.exe processes that are behaving oddly, such as those using a lot of CPU (Central Processing Unit) power or memory. Right-click on the process and select Go to Details to see what services it’s hosting. If anything looks unusual or unfamiliar, take action;
- Update your software: keeping Windows and other software up-to-date is one of the easiest ways to avoid malicious svchost.exe instances. Updates often patch security vulnerabilities that could help malware infiltrate your system;
- Enable the firewall: make sure your firewall is active and configured correctly. Windows Firewall, for example, can block unauthorized connections attempting to use svchost.exe as a gateway for malware;
- Scan regularly: schedule regular system scans with your antivirus software to detect any suspicious activity. This can prevent malware from hiding in your system under the guise of svchost.exe.
By following these steps, you can stay ahead of potential threats and ensure that svchost.exe continues functioning as it should — safely and securely.
How to remove a svchost.exe virus
If you’ve detected a malicious instance of svchost.exe on your system, it’s time to take action. Follow these steps to remove it safely and ensure your system stays protected.
-
Open the Task Manager
Start by pressing Ctrl + Alt + Delete to bring up the Task Manager. Look for any suspicious svchost.exe processes that use an unusually high amount of CPU power or memory.
-
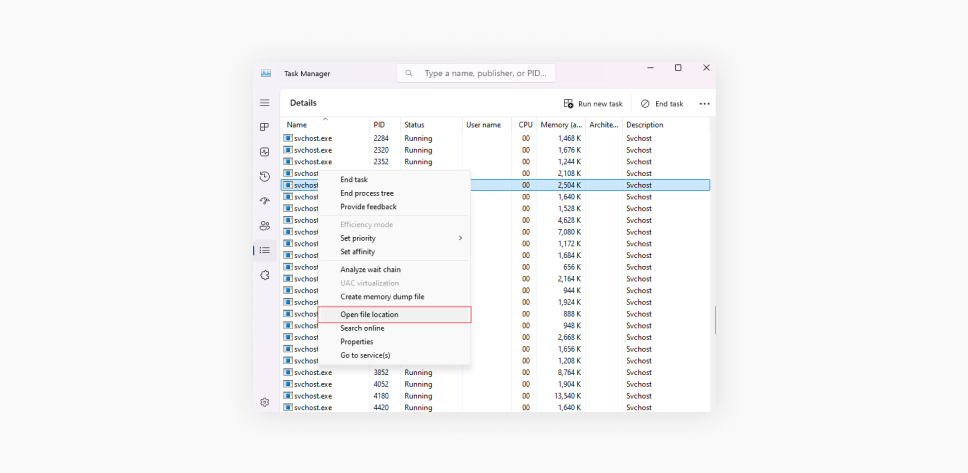
Check file location
Right-click on the suspicious svchost.exe process and select Open file location. If the file is not located in the C:\Windows\System32 folder, it’s likely malware.
-
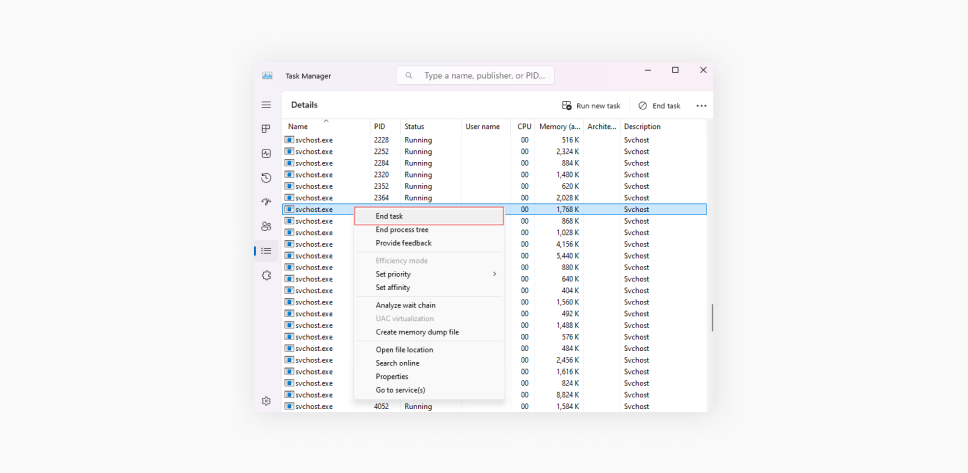
End the process
If that’s the case, go back to Task Manager, right-click on the svchost.exe process, and select End task. This will stop the malicious process from running.
-
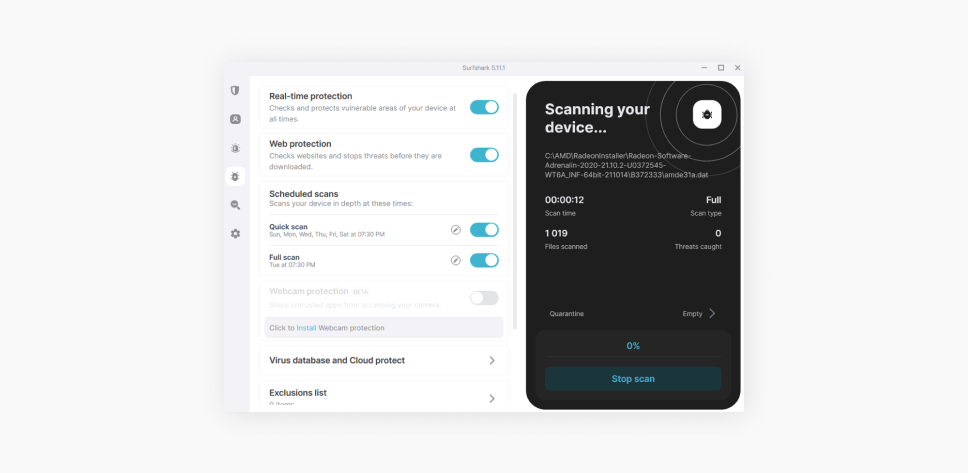
Run a full system scan
Now, open your antivirus software and run a full system scan (we recommend using Surfshark Antivirus — its malware database gets updated every three hours!). Your antivirus will identify and quarantine the threat while keeping your system secure in the future.
-
Delete the malicious file
If the antivirus doesn’t automatically remove the file, go to its location found in step 2. Delete svchost.exe manually, but only after ensuring the process is no longer active.
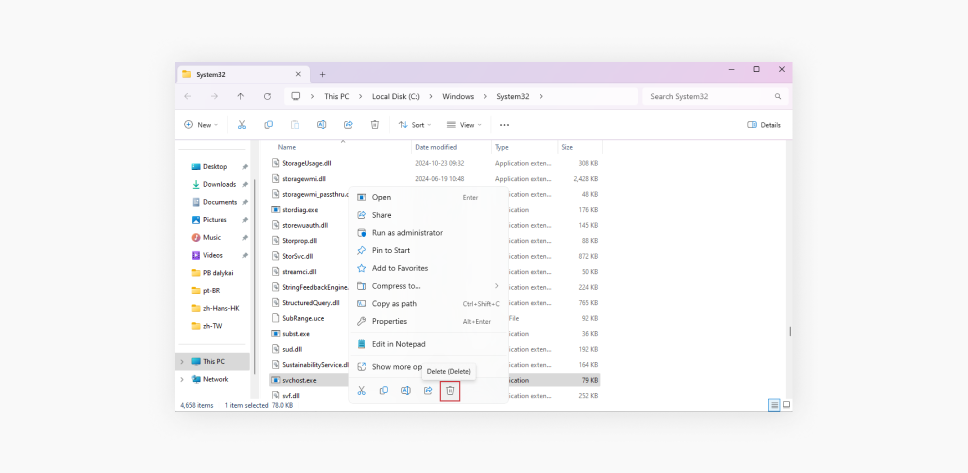
-
Update your security tools
Finally, make sure your antivirus and operating system are up-to-date. This will help prevent future attacks and keep your system secure.
Know what runs on your system
Because cyberthreats are constantly evolving, staying informed and proactive is important. Knowing what’s running on your system will help you spot unusual activity early. To stay ahead of threats, consider using security tools — like the Surfshark all-in-one suite.
FAQ
How to shut down a svchost.exe service?
To shut down a svchost.exe service, open Task Manager, right-click the specific svchost.exe process, and select End task. Be cautious, as stopping essential Windows services may cause system instability or critical function crashes.
What happens if I delete svchost.exe?
Deleting the svchost.exe file can severely damage your Windows system, as it’s responsible for running critical background services. This can lead to system crashes, errors, and the inability to boot your computer correctly.
Why is svchost.exe running multiple times?
Windows runs multiple instances of svchost.exe to separate and manage different groups of services. This approach improves system stability, efficiency, and security by isolating services from one another.
How to check if svchost.exe is infected?
You can check if svchost.exe is infected by opening the Task Manager, right-clicking the process, and selecting Open file location. If the file isn’t located in C:\Windows\System32 or consumes a lot of resources, it may be malware.


